Jan 1, 2026
What Parameters Do Patient Monitors Measure?
A standard bedside patient monitor collects critical data about the body's essential functions. These data include:
ECG (Electrocardiography): Monitors the heart's electrical activity and rhythm. The heart rate (pulse) is displayed on the screen per minute.
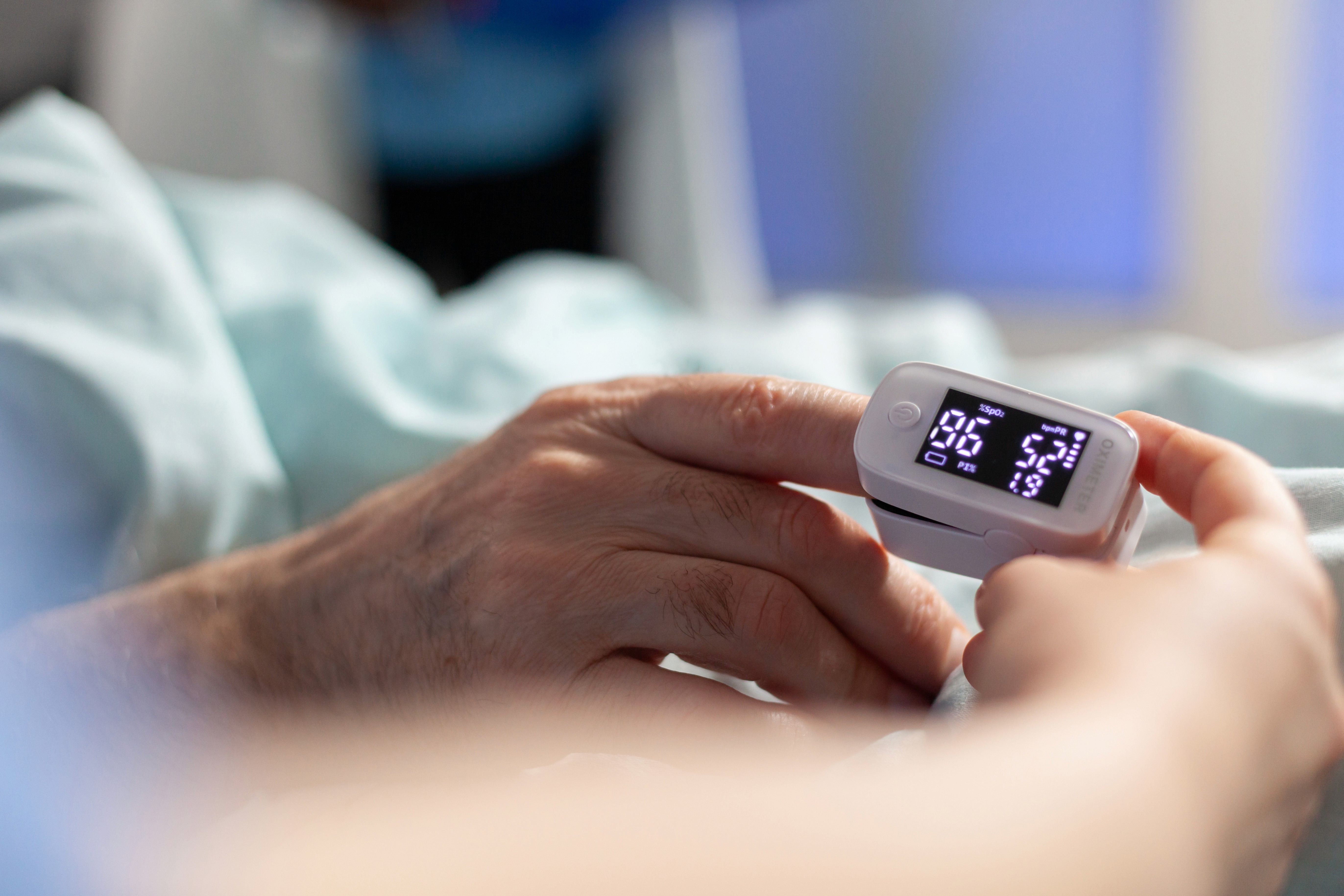
SpO2 (Oxygen Saturation): Measures the oxygen saturation in the blood. Provides information about the sufficiency of respiratory functions.
NIBP (Non-Invasive Blood Pressure): Measures the patient's blood pressure (systolic and diastolic pressure) by inflating a cuff at specific intervals.
Body Temperature: Tracks changes in the patient's body temperature.
Respiratory Rate: Indicates the number of breaths per minute.
Where Are These Systems Used?
Patient monitoring systems are standard equipment found in all medical units where close monitoring of a patient's condition is required:
Intensive Care Units: These are areas where the vital functions of critically ill patients need to be monitored every second.
Operating Rooms: The effects of anesthesia and surgical intervention on the body are monitored in real-time during surgical procedures.
Emergency Departments: Used to quickly assess the general condition of the patient at the time of initial intervention.
Inpatient Wards: Can be used for routine checks or continuous monitoring of patients undergoing treatment.





